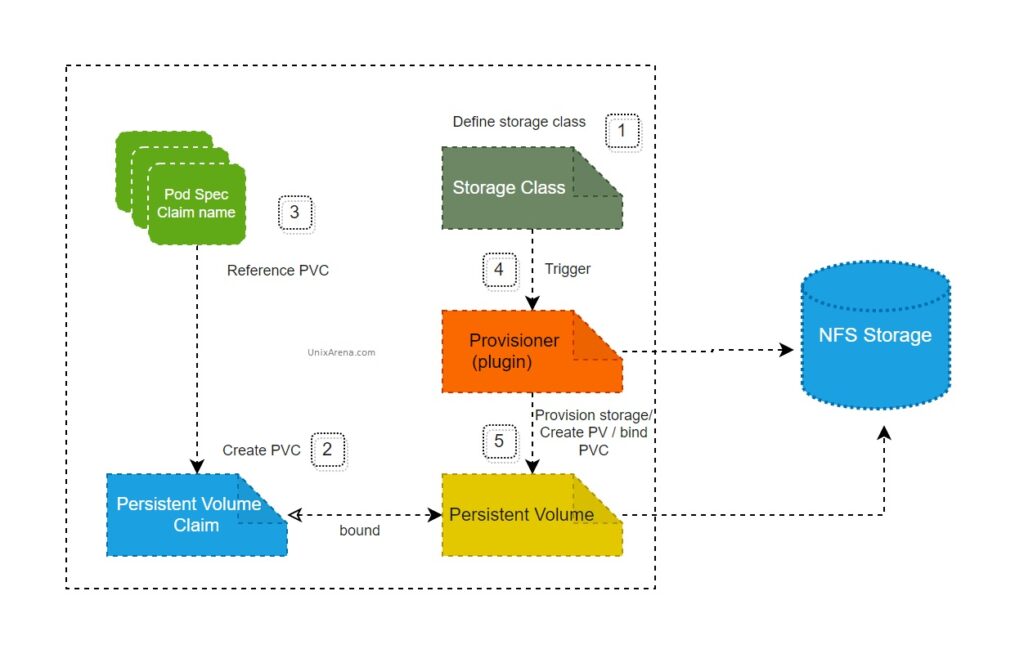
NFS subdir external provisioner is an automatic provisioner that uses your existing and already configured NFS server to support dynamic provisioning of Kubernetes Persistent Volumes via Persistent Volume Claims. This article will walk you through how to deploy NFS Subdir External Provisioner to the k8s cluster and create the PV using the NFS backend storage. We just need to ensure that the K8s cluster is having connectivity with the NFS server that you are going to use in the configuration. NFS uses port 2049 and ensures that necessary ports are open to the target.
NFS storage can be any server, storage appliances or NAS devices. For testing purpose, i have exported the Linux filesystem as NFS share.
Deploy NFS Subdir External Provisioner
1. Let’s create a service account with the name “nfs-client-provisioner”. Create a new file with the following content (ex: service_rbac.yaml).
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
2. Create the service account.
lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$ kubectl apply -f service_rbac.yaml rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner configured lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$
3. Verify the newly created service account.
lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$ kubectl get sa nfs-client-provisioner NAME SECRETS AGE nfs-client-provisioner 1 5d21h lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$
4. Create a new storage class using the following file. (ex: class.yaml)
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: nfs-client
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
provisioner: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner # or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
parameters:
archiveOnDelete: "false"
lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$ kubectl apply -f class.yaml
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/nfs-client configured
lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$
4. Verify the newly created storage class.
lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$ kubectl get sa nfs-client-provisioner NAME SECRETS AGE nfs-client-provisioner 1 5d21h lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$
5. Let’s create the deployment file. Update your NFS server IP and share path. My NFS server IP is “192.168.23.132” and path is “/mnt/nfs_share”
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
image: k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.2
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 192.168.23.132
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /mnt/nfs_share
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 192.168.23.132
path: /mnt/nfs_share
6. Create the deployment for “nfs-subdir-external-provisioner” .
lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$ kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml deployment.apps/nfs-client-provisioner configured lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$
7. Verify the nfs-subdir-external-provisioner by listing all the objects from the default namespace. (Note: I have used the default namespace for the deployment)
lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$ kubectl get all NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/nfs-client-provisioner-6c9675b6bb-82ggc 1/1 Running 17 (23m ago) 5d21h NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.233.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 8d NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/nfs-client-provisioner 1/1 1 1 5d21h NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/nfs-client-provisioner-6c9675b6bb 1 1 1 5d21h lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/subdir-nfs$
Here we could see that nfs-client-provisioner is up and running.
Test the NFS client provisioner
8. Let’s test the dynamic nfs client provisioned. Create the following manifest to provision volume with a size of 512MB.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc-nfs-pv2
spec:
storageClassName: nfs-client
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 500Mi
9. Create the pv & pvc using the manifest.
lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/kubernetes/yamls$ kubectl create -f 4-pvc-nfs.yaml persistentvolumeclaim/pvc-nfs-pv2 created lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/kubernetes/yamls$ kubectl get pv,pvc NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE persistentvolume/pvc-9c7a80a1-9da9-4e3e-be0e-969f41ad437e 500Mi RWX Delete Bound default/pvc-nfs-pv2 nfs-client 11s NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE persistentvolumeclaim/pvc-nfs-pv2 Bound pvc-9c7a80a1-9da9-4e3e-be0e-969f41ad437e 500Mi RWX nfs-client 11s lingesh@uamaster1:~/nfs/kubernetes/yamls$
We have successfully create pv and pvc using the nfs backend storage. Let’s try to attach pv to one of the deployment pod.
10. Create the deployment file for nginx using below manifest to test the pvc to attach the volume to the pod.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
volumes:
- name: task-pv-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc-nfs-pv2
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/test"
name: task-pv-storage
The above manifest will create new nginx deployment and attach the pvc “pvc-nfs-pv2” . This volume will be mounted under “/test” in the pod.
11. Deploy nginx using kubectl command.
lingesh@uamaster1:~$ kubectl create -f test_nginx.yaml deployment.apps/nginx-deployment created lingesh@uamaster1:~$ kubectl get all NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/nginx-deployment-6b5b759665-m49d4 1/1 Running 0 5s NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/nginx-deployment 1/1 1 1 5s NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/nginx-deployment-6b5b759665 1 1 1 5s lingesh@uamaster1:~$
12. Let’s verify the mount points in pod.
lingesh@uamaster1:~$ kubectl exec nginx-deployment-6b5b759665-m49d4 -- df /test Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on 192.168.23.132:/mnt/nfs_share/default-pvc-nfs-pv2-pvc-0c87433b-61ad-4b48-97a0-b8c62ab56517 30898176 12501504 16995840 43% /test lingesh@uamaster1:~$
We have successfully mounted the NFS storage backend pv to pod. Hope this article is informative to you. In upcoming article, we will see how can we use the cloud natvie storage plugins for the kubernetes cluster.