How to use AWS SSM Patch Manager? AWS SSM Patch Manager provides a secure patching experience for both Windows and Linux operating systems. Like other AWS services, AWS SSM can be easily integrated with other services like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), AWS CloudTrail, and Amazon EventBridge for notification and the ability to audit usage. Overall, this AWS native solution brings centralized management for patching your fleet of Amazon EC2 Windows and Linux instances or your on-premises servers and virtual machines (VMs). To schedule the reoccurring patching using SSM, check out this article.
Note: AWS does not test patches for Windows Server or Linux before making them available in Patch Manager. Also, Patch Manager doesn’t support upgrading major versions of operating systems, such as Windows Server 2016 to Windows Server 2019, or RHEL 7 to RHEL 8.
How Patch Manager works ?
- Use pre-defined patch baseline, or create your own baseline based on your complaince requirement.
- Organize instances into patch groups using tags (Optional)
- Automate the patching schedule for each environment by using Maintenance Windows
- Monitor patch status to ensure compliance. This can be tracked in complaince tab for overall environment.
Predefined Patch Baseline:
1. Login to AWS console with required SSM privileges.
2. Navigate to Systems Manager.
3. In Systems Manager – > Under Node Management, Click Patch Manager.
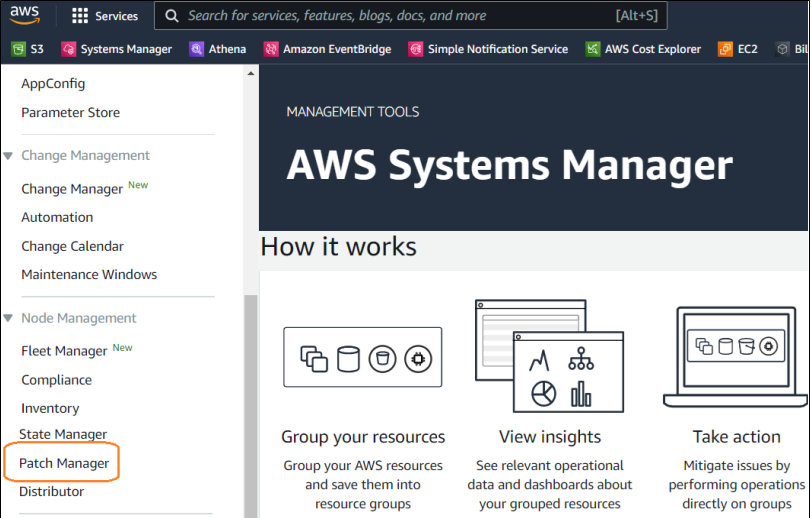
4. Click on “view predefined patch baselines“.
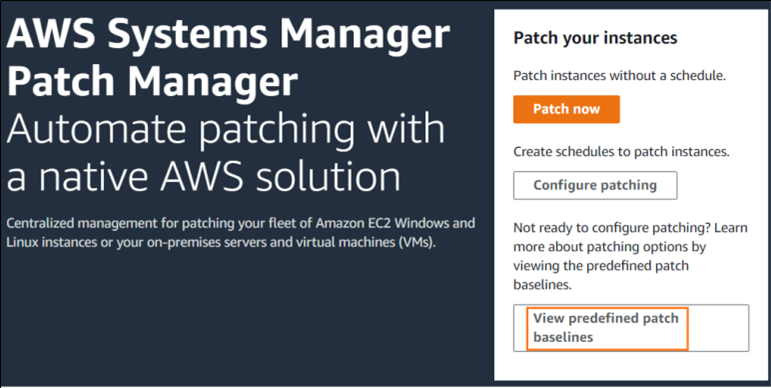
5. Here you can see the pre-defined default patch baselines for windows and Linux operating systems including Redhat.
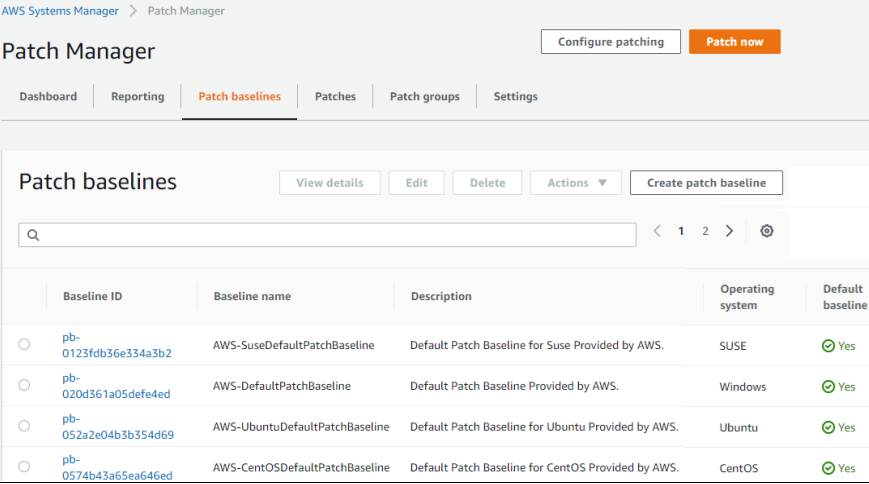
These patch baselines can be directly used to patch the EC2 instances and ONPREM instances.
Default Patch baselines
| Operating Systems | Patch Baselines |
| Microsoft Windows Servers | AWS-DefaultPatchBaseline |
| SUSE Linux | AWS-SuseDefaultPatchBaseline |
| Redhat Enterprise Linux | AWS-RedHatDefaultPatchBaseline |
| Mac OS | AWS-MacOSDefaultPatchBaseline |
| Amazon Linux | AWS-AmazonLinuxDefaultPatchBaseline |
| Amazon Linux 2 | AWS-AmazonLinux2DefaultPatchBaseline |
| Ubuntu | AWS-UbuntuDefaultPatchBaseline |
| Oracle Linux | AWS-OracleLinuxDefaultPatchBaseline |
| Debian | AWS-DebianDefaultPatchBaseline |
| CentOS | AWS-CentOSDefaultPatchBaseline |
| Raspberry Pi OS | AWS-RaspbianDefaultPatchBaseline |
How to Patch Windows/Linux instances using the default patch baseline ? (AD-HOC)
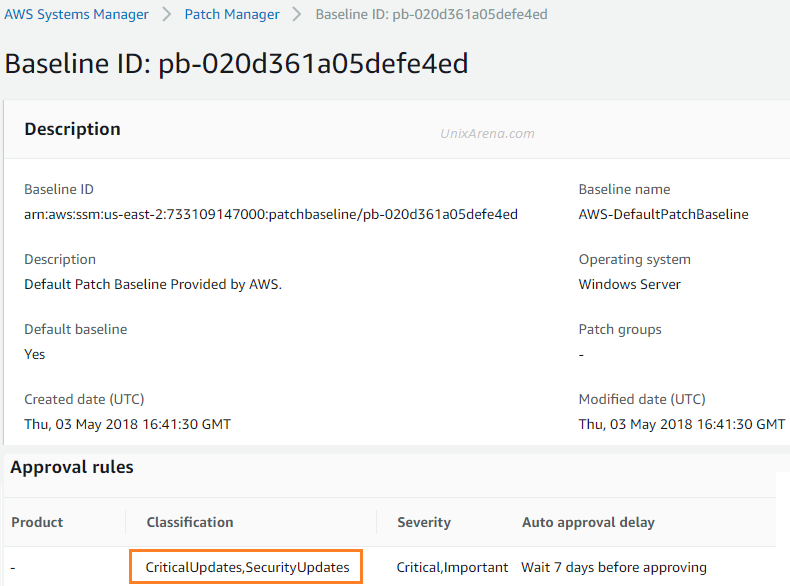
1. From the pre-defined patch baseline, Click on “AWS-DefaultPatchBaseline” which is used to patch the windows instances. Similarly, you can check for the respective Linux flavors to know what patches will be installed as part of the default patch baseline.
2. Here you can see the type of patches which will be updated when you use the default baseline. Default baseline installs critical updates and security updates only. If you would like to customize this, you need to create your own patch baseline. The same applies to Linux patch baselines as well.
3. Go back to patch manager using breadcrumb navigation. Click on “Patch now“.

4. Here is the ad-hoc method to install the patches on the instances. AWS automatically selects the default baseline document for the respective instance’s OS type.
- Select patching operation as “Scan and Install“
- Schedule a reboot time.
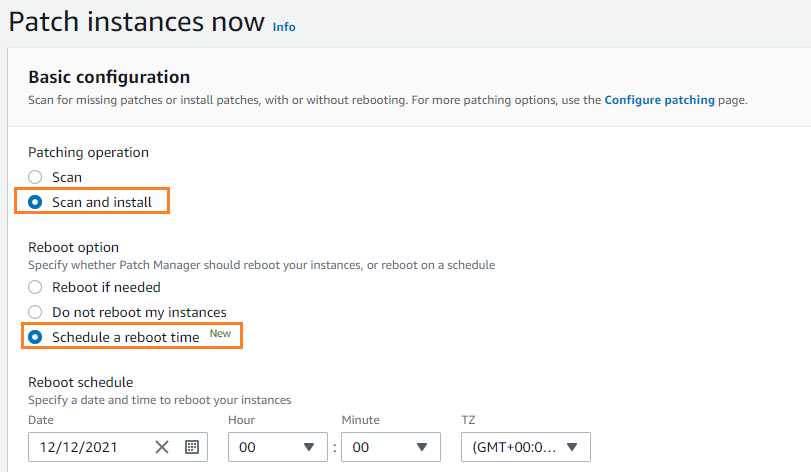
5. Specify the target environment using tags or resource groups. Here I have used the tag “Environment: DEV”. Once you have submitted the job, it will create a job id.
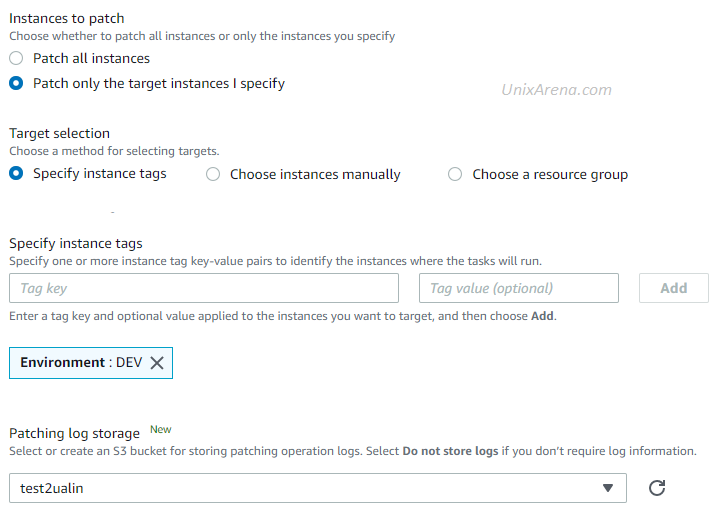
6. Here is the association id for the patching task. You can click the “association ID” link to check the target servers.
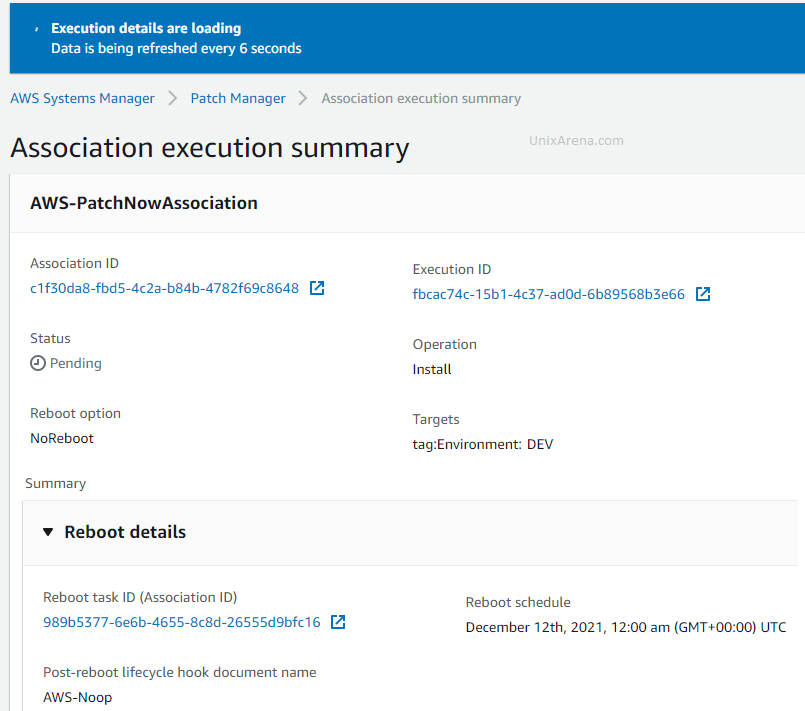
The SSM state manager invokes the run command to install the patches.
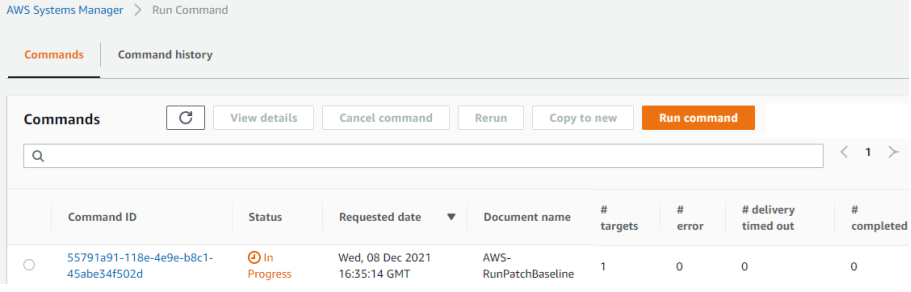
7. Once the job is completed, you can view the job output.
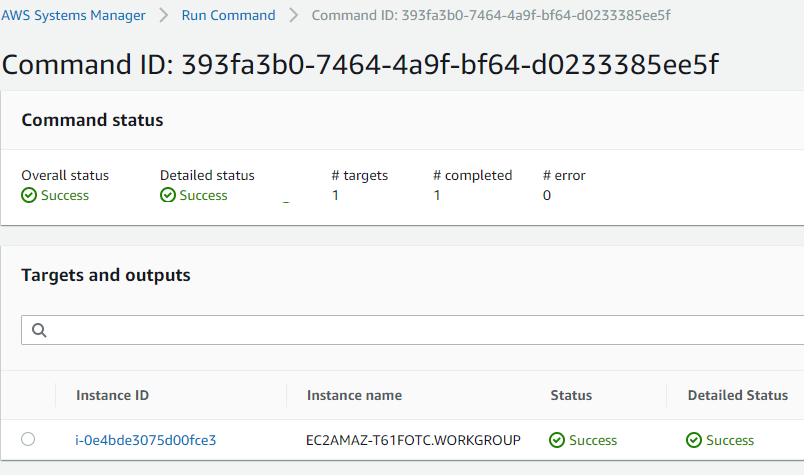
We have successfully installed the patches on the OS instances using the “Patch now” ad-hoc method. In the upcoming article, will see how to group the instances using patch group, how to set the predefined maintenance window, and how to get the consolidated compliance view in the SSM dashboard.
Leave a Reply